Emotion: Circuit Level: The Limbic System


- -- The triurne brain: (MacLean, 1985) decomposes
the brain into 3 evolutionary distinct 'sub-brains': Reptilain, early mammalian
(limbic system), and late mammalian brains.
-- The visceral brain (MacLean, 1949), or limbic
system (MacLean 1952) is introduced in relation
with the Papez circuit . It is defined around
the hippocampus (including hippocampal and dentate giri, and amygdala).
It is involved in self-preservation and preservation of the species (MacLean,
1958). The hippocampus is the locus of sensory integration and therefore
of the experience of emotion. Its projections to the hypothalamus give
rise to emotional expressions.
(see also (LeDoux, 1987))
- An anatomical redefinition of the limbic system (Swanson
1983).
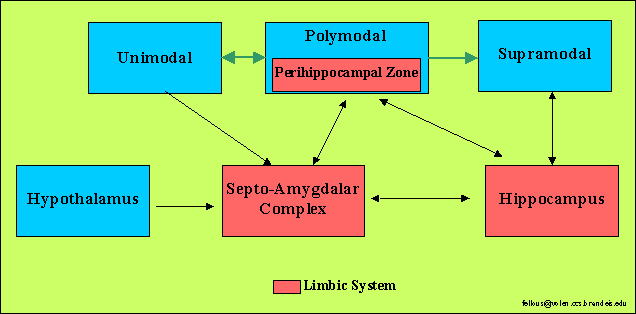
- Lopes da Silva et al. (1990) offer a hippocampus-centered
view of the limbic cortex.On the anatomical and cytoarchitectural grounds,
they propose that the central components of the limbic cortex are the hippocampal
formation (dentate, ammon's horn, subiculum), the indusium griseum
and the tenia tecta.The periphereal components are the pre/post/para subiculum
(area 27, 48 and 49 resp), the entorhinal cortex (28), the medial perirhinal
cortex (35a), the granular part of the posterior cingulate cortex (29c),
the ventral part of the anterior cingulate cortex (24a-c) and the infralimbic
cortex (25).
- An attempt to integrate psychoanalytical and neurobiological thought
on drives, affects behavior and learning: The limbic system (Schwartz,
1987)
For More Information
Peer reviewed and published articles on line:
Editor: Jean-Marc Fellous
